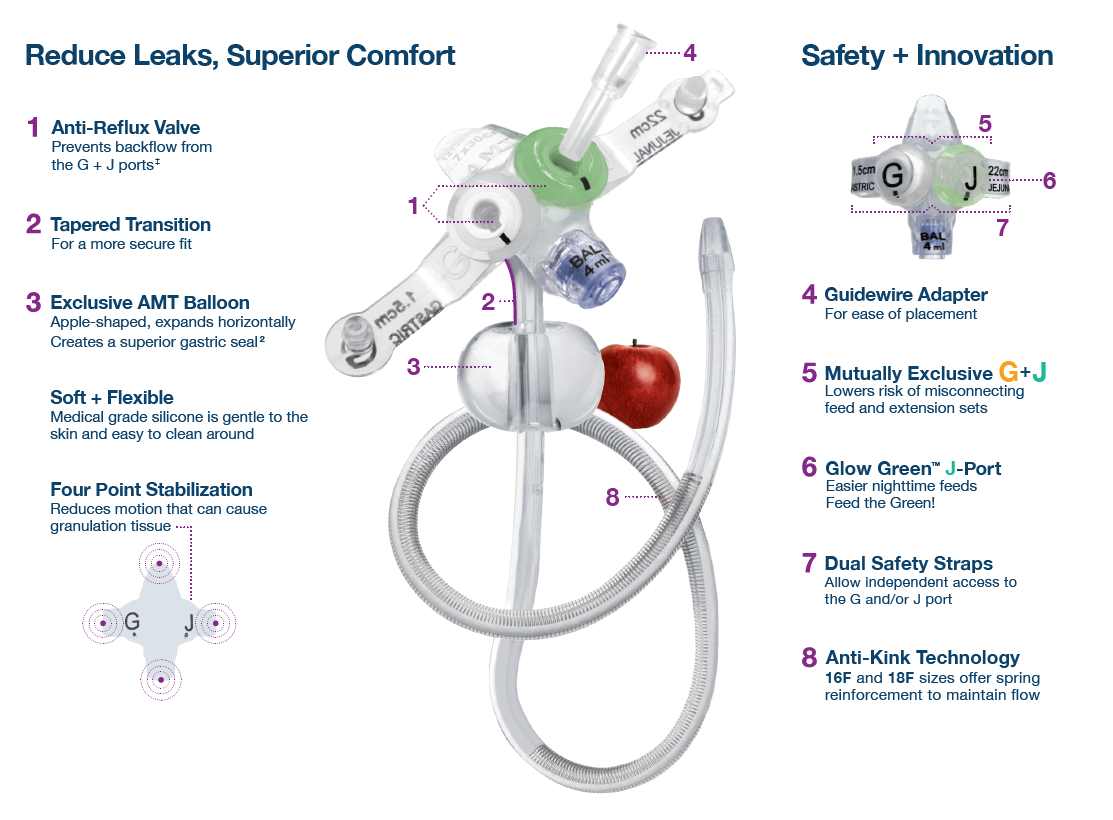
Image Source: Google
Jejunal feeding tubes are a crucial medical intervention for patients who are unable to consume food orally. Whether you are a patient about to have a jejunal feeding tube inserted or a caregiver providing support to someone with this device, understanding how to navigate the world of jejunal feeding tubes is essential.
This comprehensive guide aims to provide you with the necessary information to help you manage jejunal feeding tubes effectively and ensure the well-being of the patient.
What is a Jejunal Feeding Tube?
A jejunal feeding tube is a type of enteral feeding tube that is inserted through the nose, mouth, or abdominal wall into the jejunum, which is the second part of the small intestine. This type of feeding tube allows for the delivery of nutrients directly into the small intestine, bypassing the stomach. Jejunal feeding tubes are typically used when a patient has difficulty tolerating feeding into the stomach, such as in cases of gastric motility issues, severe reflux, or gastroparesis.
Types of Jejunal Feeding Tubes:
- Nasojejunal tube: Inserted through the nose and passed into the jejunum.
- Orojejunal tube: Inserted through the mouth and passed into the jejunum.
- Percutaneous endoscopic jejunostomy (PEJ) tube: Inserted directly through the abdominal wall into the jejunum.
- Surgical jejunostomy tube: Surgically placed into the jejunum.
Indications for Jejunal Feeding Tubes
Jejunal feeding tubes are recommended for patients who have specific medical conditions or circumstances that necessitate bypassing the stomach for enteral feeding. Some common indications for jejunal feeding tubes include:
- Gastroparesis
- Severe reflux
- Neurological conditions affecting swallowing
- Severe malnutrition
- Gastrointestinal motility disorders
Insertion and Care of Jejunal Feeding Tubes
Insertion Process:
The insertion of a jejunal feeding tube is typically performed by a healthcare professional, such as a gastroenterologist or interventional radiologist. The specific insertion method will depend on the type of jejunal feeding tube being used. It is essential to follow the healthcare provider's instructions before, during, and after the insertion procedure to minimize the risk of complications.
Care and Maintenance:
Proper care and maintenance of a jejunal feeding tube are crucial to prevent infections and complications. Some important tips for caring for a jejunal feeding tube include:
- Regularly clean around the insertion site with soap and water.
- Secure the tube to prevent accidental dislodgement.
- Flush the tube with water before and after each feeding or medication administration.
- Monitor for signs of infection, such as redness, swelling, or discharge at the insertion site.
- Follow the healthcare provider's instructions for tube flushing, feeding, and medication administration.
Potential Complications of Jejunal Feeding Tubes
While jejunal feeding tubes are generally safe and well-tolerated, there are some potential complications that patients and caregivers should be aware of. These may include:
- Tube dislodgement
- Infection at the insertion site
- Tube blockage
- Aspiration pneumonia
- Incorrect tube placement
- Skin irritation or breakdown around the insertion site
Managing Feeding and Medication Administration
Properly managing feeding and medication administration through a jejunal feeding tube is essential for ensuring the patient's nutritional needs are met and maintaining their overall health. Some key considerations for managing feeding and medication administration include:
- Use only liquid forms of medications.
- Administer medications one at a time, flushing the tube with water between each one.
- Follow a feeding schedule provided by the healthcare provider.
- Monitor for signs of intolerance to the feeding formula.
- Adjust the feeding rate as needed based on the patient's tolerance and nutritional requirements.
Consulting with Healthcare Providers
It is crucial to maintain open communication with the healthcare team involved in the care of a patient with a jejunal feeding tube. Regular follow-up appointments with the healthcare provider, gastroenterologist, or dietitian can help ensure the proper functioning of the jejunal feeding tube and address any concerns or complications promptly.
